The Gupta’s Empire
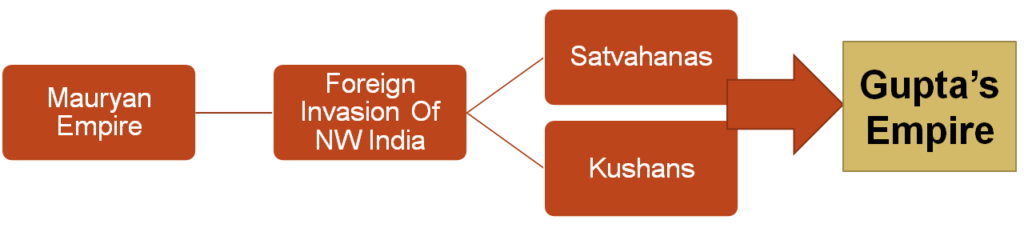
After the decline of the Kushanas, north India witnessed the rise of the Gupta dynasty
The Gupta period marks the important phase in the history of ancient India. The long and efficient rule of the Guptas made a huge impact on the political, social and cultural sphere.
Though the Gupta dynasty was not widespread as the Maurya Empire, but it was successful in creating an empire that is significant in the history of India.
They operated from eastern U.P. and Bihar which was very fertile.
They could also exploit the iron ores of central India and Bihar to their advantage.
Their period was marked by great progress in art, architecture and literature. They ruled up to circa A.D.550.
The Gupta period in ancient India is referred to as the “Golden Age” because of the numerous achievements in the field of arts, literature, science and technology. It also brought about the political unification of the subcontinent
After their collapse there emerged various regional kingdoms in north India
The Gupta Dynasty
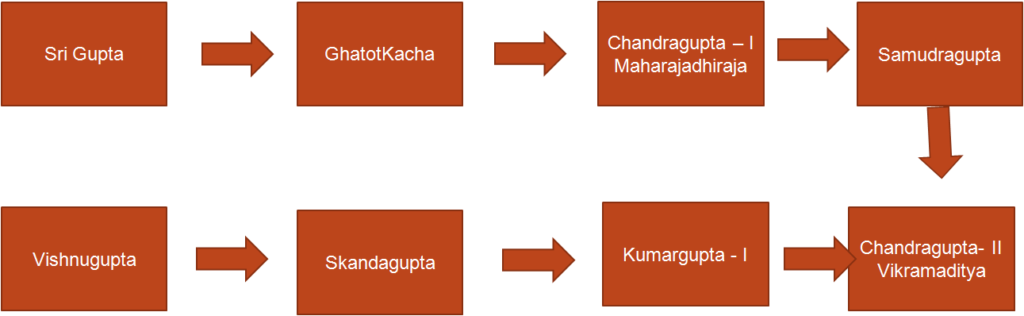
The Gupta’s Empire -Chandragupta I (320-330 AD)
1st to be called as Maharajadhiraj (Great king of kings) •
Married Lichhavi princess which gave him strength & prestige •
The marriage alliance with Kshatriyas gave social prestige to the Guptas who were Vaishyas.
This event is recorded in a series of gold coins issued by Chandragupta
Started the Gupta era as a mark of his ascension to the throne
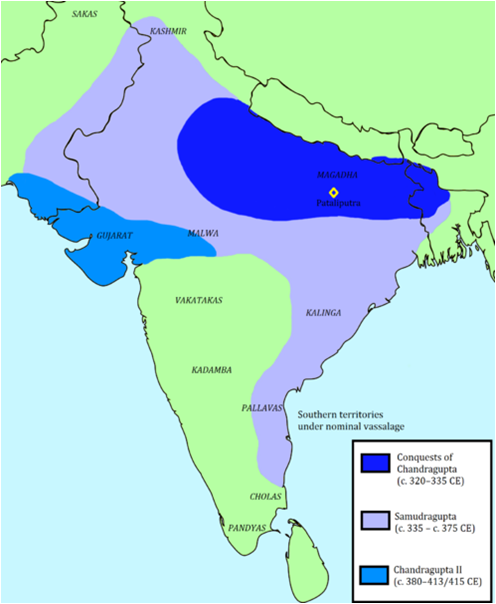
Chandragupta I was able to establish his authority over Magadha, Prayaga,and Saketa.
The Gupta’s Empire – Samudragupta (C.E. 335 – 375)
Referred to as the “Napoleon of India” by historian Vincent. A. Smith.
He was magnicent dynasty (Gupta Empire) builder and great administrator and greatest among Guptas.
His achievements are recorded in a long inscription (Prayag Prashasti), written in pure Sanskrit by his court poet Harisena. The inscription is engraved on a Pillar at Allahabad
He performed an Asvamedha, adopted title “Parakramanka”..
He wrote poems and earned the title “Kaviraja”.
He minted gold coins with his own image and Laxmi’s image, Garuda, Ashvamedha yagya & playing veena
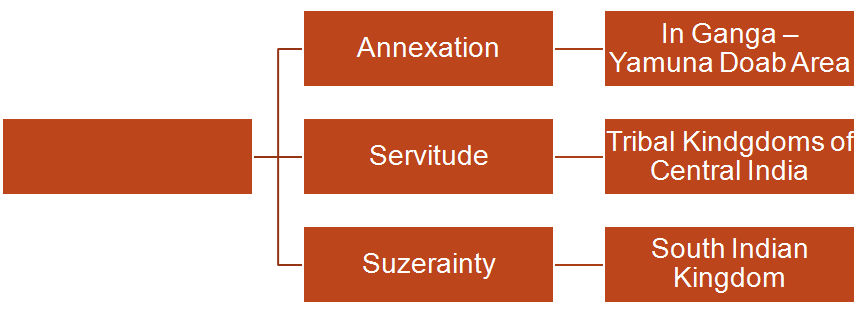
Samudragupta adopted different policy of control and administration for different areas he conquer depending the location from capital , geographical factors , trade routes etc.
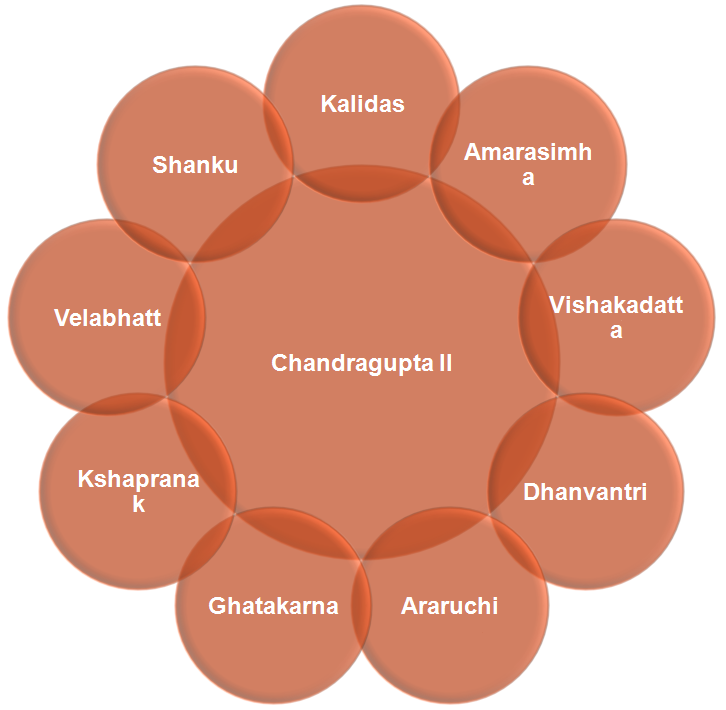
The Gupta’s Empire -Chandragupta II (380 C.E. to 415 C.E.):
He was also known as Chandragupta Vikramaditya i.e. the one who is as powerful as the sun.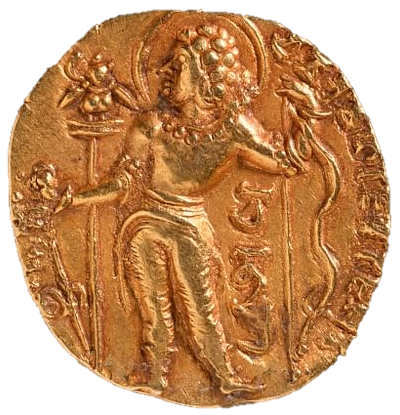
He not only extended his father’s empire but also consolidated his position through matrimonial alliances with other royal dynasties of the period
His greatest military achievement was his victory over the Shaka kings who were ruling in western India for the last three hundred years. This conquest made Gupta empire reach up to the western coast.
Fahien, the Chinese traveler visited India during his time (399 A.D.-410 A.D.)
An iron pillar inscription at Mehrauli in Delhi indicates that his empireincluded even north-western India and Bengal
He was the first Gupta king who issued silver coins
According to drama ― “Devichandraguptam” written by Vishakhadutta is about Chandragupta‘s succession by displacing his brother Ramagupta..
Ramaupta ruled for very short period .
Ujjain became 2nd capital of Guptas, 1st being Pataliputra (Patna today)
Exploits written on – Mehrauli Iron pillar Delhi
The Gupta’s Empire – Kumaragupta (415 C.E. to 455 C.E.)
He was able to maintain the empire built up by his father but during the later part of his reign there was a threat from the Hunas of Central Asia
17 Inscriptions mainly in Mandasur M.P. and Mathura written in Sanskrit give evidence of his reign.
He adopted the title of Mahendraditya.
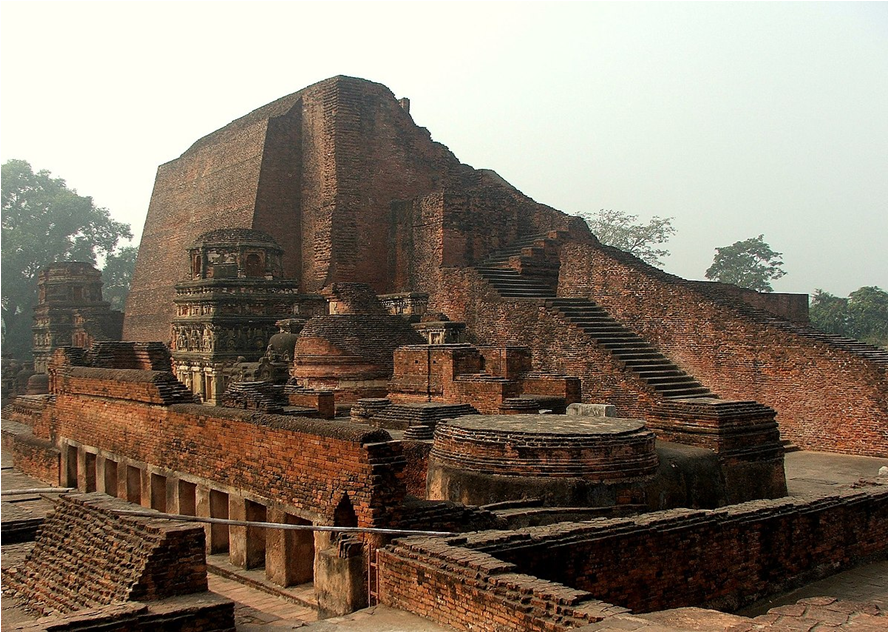
Nalanda Buddhist Monastery (later became Nalanda University) was built during his period.
The Gupta’s Empire – Skandagupta (455 C.E. – 467 C.E.)
He was the last greatest Gupta ruler.
He assumed the titles Parambhattaraka, Paramdevta, Maharajadhiraj, etc.
He successfully resisted the Huns invasion.
The Junagadh inscription mentions the restoration of the embankment of Sudarshana Lake.
The Bhitari inscription records the career of Skandagupta.
He erected a pillar of victory surmounted by the statue of God Vishnu.
He issued the Lion type coins
The Gupta’s Empire – End time
Purugupta ascended the throne after Skandagupta. Vishnugupta was the last king.









No comment