Small Causes Court
Section- 7 & 8 of CPC, 1908

Small Causes Court
Section- 7 & 8 of CPC, 1908 – History
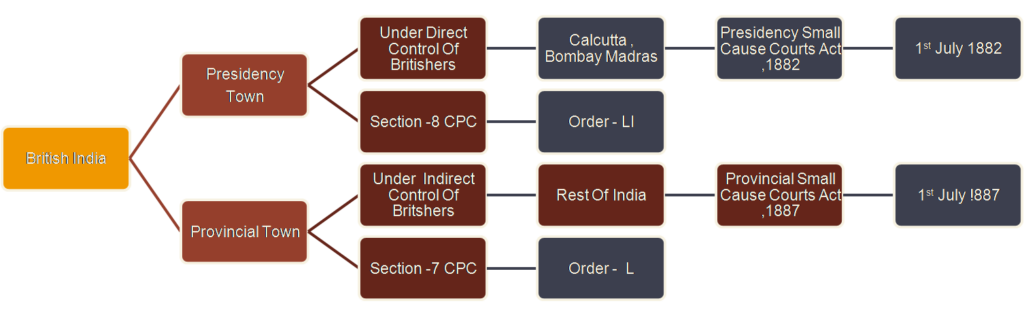
One of the many judicial institution brought into India by the British Administration was the small cause court. Its history dates back to the year 1753 when the East India Company directed the government at Calcutta (Fort William) to set up a court for the summary(minimal procedure) disposal of petty claims.
This was the oldest Court in British Empire. It was established by Charter of George the second on 08.01.1753. Such Courts were established only in three presidency towns of Calcutta, Madras and Mumbai and they were initially known as “Courts of Requests”. Later on in 1882 when the Presidency Small Causes Courts Act was brought into force, these Courts were named as Small Causes Courts. The Judges of Courts of Small Causes were being appointed by Governor in Council. Small Causes Courts were to follow practice and procedure subject to approval of respective Supreme Courts in presidency towns
Small Causes Court
Section- 7 & 8 of CPC, 1908 – Purpose
The Purpose behind the establishment of the court of request (later small cause court) was to provide for the expeditious and final settlement of petty demands, omitting most of the formalities that delayed the disposal of regular suits
Order-51 of Civil Procedure Code exempts application of the orders in schedule-1 to it, except few orders therein to any suit or proceeding in any Court of Small Causes established in the said towns and thus the Courts of Small Causes are expected to advance justice without adhering much to the tricky procedural laws and complicities. Rules framed by the Hon. High Court have made some orders and rules in C.P.C applicable. As such trials are conducted in the court of small causes Mumbai by following rules framed under the Presidency small cause courts Act 1882. The object obviously is to advance justice speedily
Small Causes Court
Relation With Mahatma Gandhi
 Mahatma Gandhi made his debut as a Lawyer in Mumbai Small Causes Court in 1891. Gandhi ji as a young lawyer noted down all his struggles in his autobiography
Mahatma Gandhi made his debut as a Lawyer in Mumbai Small Causes Court in 1891. Gandhi ji as a young lawyer noted down all his struggles in his autobiography
Link – https://www.mkgandhi.org/autobio/chap28.htm
Small Causes Court
Important Points
THE PRESIDENCY SMALL CAUSE COURTS ACT, 1882
- An Act to consolidate and amend the law relating to the Courts of Small Causes established in the Presidency towns
- Small Cause Court and Registrar defined Under Section – 4
- Court to be deemed under superintendence, etc., of High Court – Section -6
- Registrar may be invested with powers of a Judge in suits not exceeding twenty rupees.— Section – 14
- Section -18 – Suits in which Court has jurisdiction.— when the amount or value of the subject-matter does not exceed two thousand rupees
- Section -19 – Suits in which Court has no jurisdiction
- assessment or collection of the revenue
- any act done by or by order of the Central /State Govt
- any act ordered or done by any Judge or judicial officer
- recovery of immovable property
- partition of immovable property
- partition of immovable property
- dissolution of partnership
- restitution of conjugal rights
- Divorce
- possession of a hereditary office
Important Points
THE PROVINCIAL SMALL CAUSE COURTS ACT, 1887
- An Act to consolidate and amend the law relating to Courts of Small Causes established beyond the Presidency-towns.
- “Court of Small Causes” is defined under section -4
- State Government will establish the Small Cause Courts. Section – 5
- .In case of difference among two judges of Bench , they refer the matter if –
- a question of law
- usage having the force of law
- in construing a document the construction of which may affect the merits,
- Section -12 – defines Register – Jurisdiction upto INR – 20/- , he shall be the chief ministerial officer of the Court
- Section – 15 – Cognizance of civil suits upto five hundred rupees . State Gov. can increase upto the level of one thousand rupees.
- Trial of suits by Registrar – Section -18 – same value of decree even if tried by registrar
- Passing of decrees by Registrar on confession – Section -20 –Pass Decree against the defendant, upon the admission, a decree which shall have the same effect as a decree passed by the Judge.
- Appeal –Section -24 – From Small Cause Court to District Court.
- Section – 30 – Abolition of Courts of Small Causes.—The State Government may, by order in writing, 1 abolish a Court of Small Causes
- SUITS EXCEPTED FROM THE COGNIZANCE OF A COURT OF SMALL CAUSES – SCHEDULE -2
-
- a suit for the possession of immovable property or for the recovery of an interest in such property;
- a suit for the partition of immovable property;
- Mortgage, Foreclosure, Redemption
- assessment, enhancement, abatement or apportionme nt of the rent of immovable property;
- a suit for the recovery of rent, other than house -rent, unless the Judge of the Court of Small Causes has been expressly invested by the State Government with authority to exercise jurisdiction with respect thereto








No comment