Vedic Age refers to that period when the Aryan wave after wave migrated to India.
Early Vedic age – 1500 – 1000 BC
Later Vedic age – 1000 – 600 BC
Aryan – person of high birth
Veda – To know / Superior knowledge
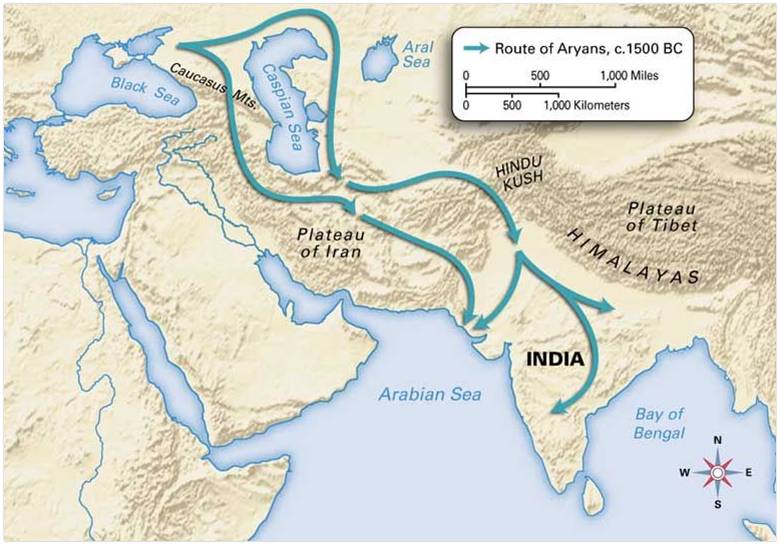
It is generally agreed that Aryans originally lived somewhere in Steppes stretching from southern Russia to central Russia. The consensus of opinion is that originally they lived somewhere in the East of Alps. On their way to India, Aryans first appeared in Iran and a little later than 1500 BC they appeared in India.
Kassite Inscription of about 1600 BC and Mittani Inscription of 1400 BC found in Iraq bear some Aryan names, which suggest that from Iran a branch of Aryans moved towards west.
The Rig Veda has many things in common with the Avesta – the oldest text in Iranian language
Origins of Aryans
- Central Asia – Max Mueller
- Tibet- Dayanand saraswati
- Arctic – BG Tilak
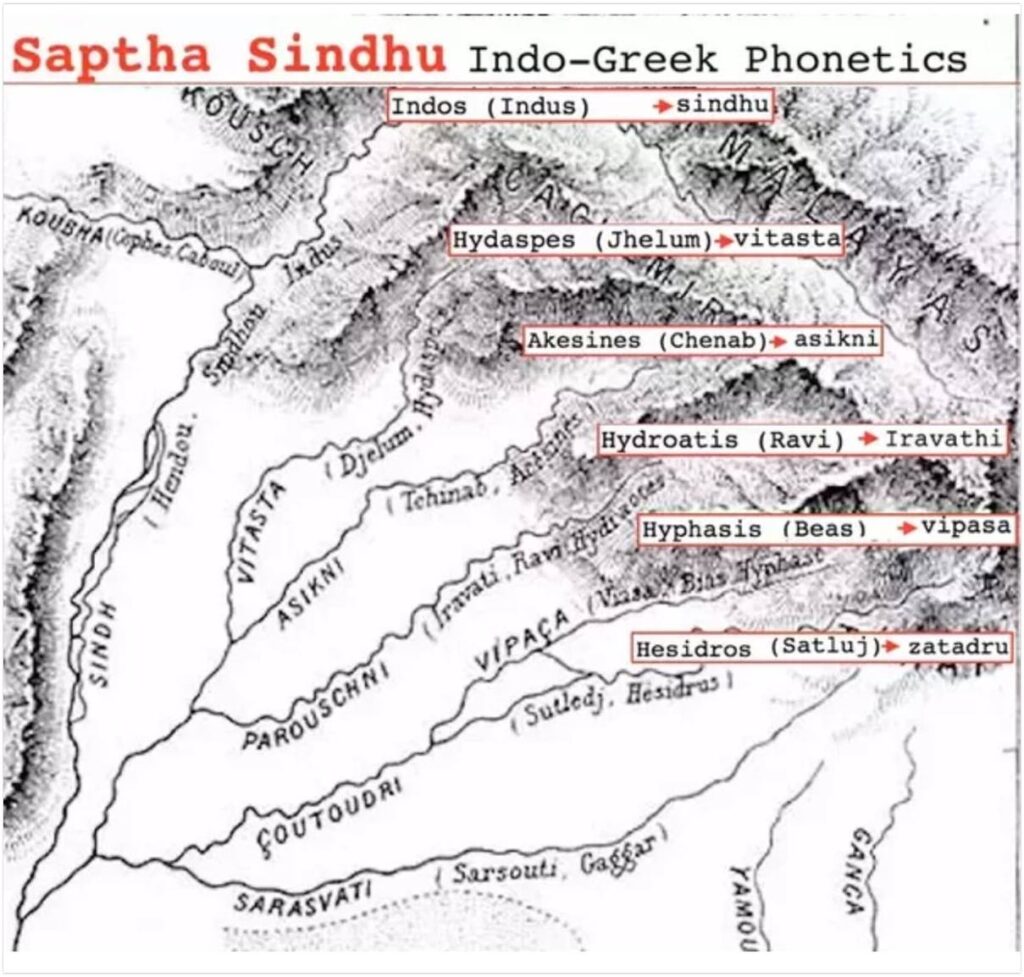
- AC Das – Sapt Sindhu
- McDonnell and Gibbs – Austria Hungary
- Belfy – Russian Steppes
- Most accepted – Great steppes of Eurasia
- Boghazkoi – Central Asia shows inscriptions of Indra Varun from 1400 BC
Settlements of Aryans
Migrations from central Asia to south Asia (India) and towards Europe •
Between 2000 and 1500 BC they started settling in the Sapta Sindhu(Punjab) region •
It was NOT an INVASION but wave after wave of MIGRATION •
Slowly settled in entire northern India • Dasa/Dasyu – conquered natives
Sources of Aryans
- All knowledge of Aryans from Vedas especially Rigveda (1500-1000 BC)
- Language – SANSKRIT
- Upanishads and later 3 Vedas (1000-500 BC)
- Upanishads – ‘to sit near someone’ – philosophy and spiritual knowledge – 108 in number
- Mundaka Upanishad – ‘Satyamev jayate’
- Puranas – History, genealogies ,philosophy , cosmology, 18 in total
- Ochre colored Pottery
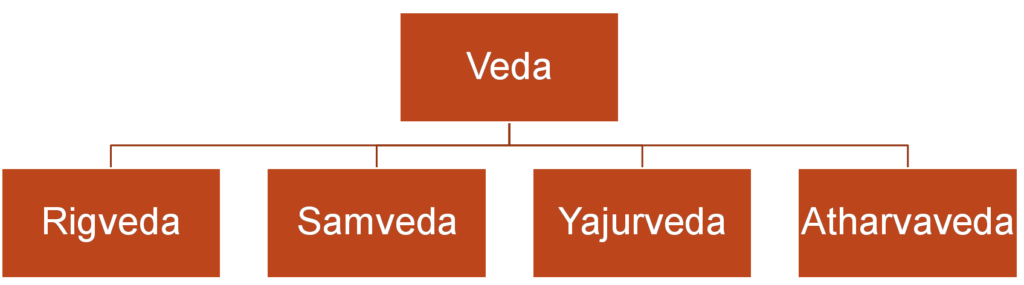
- Rigveda – Prayer Hymns
- Samveda – chants and music
- Yajurveda – Yajna, rituals and religious practices
- Atharvaveda- spells and charms to ward off evil, medicine
- Mandals- chapters/divisions
- Gaytri mantra – prayer to Savitri – 3 rd mandal of Rig Veda
- Veda means ‘Knowledge par excellence’
Social life of Aryans
Clan based kinship • Tribe – ‘jana’ *NO JANAPADA in early vedic age+ •
Patriarchal society •
Women enjoyed honorable status – could receive education and offer sacrifices, widow remarriage present, child marriage absent •
Class division in society – 4 varnas developed
VARNA – ‘color/outward appearance’ Purusa sukta of Rigveda describes the varna origins (believed to be inserted later )
Brahmin – priest, scholars
Kshatriya – warriors, rulers, administrators
Vaishya – Traders, farmers
Shudra – Servants, Laborers in fields, dasa/Dasyu
These were CLASS, NOT CASTE • Rigid hierarchy •
No inter marrying and inter dining
Foods of Aryans
Wheat barley
Meat – fish birds goat sheep
Drinks – ‘Soma’ exhilarating drink from a mountain plant(probably from Kashmir)
Polity of Aryans
The chief was the protector of the tribe or Jana.
However, he did not possess unlimited powers for he had to reckon with the tribal Assemblies.
Sabha, Samiti, Vidhata and Gana were the tribal Assemblies.
Of these, Vidhata was the oldest. These assemblies exercised deliberative, military and religious functions.
The two most important Assemblies were the Sabha and Samiti. Samiti was general in nature and less exclusive than Sabha.
Women attended Sabha and Vidhata in Rigvedic times.
There were a few non-monarchical states {ganas), which are described whose head was Ganapati or Jyestha.
Wars of Aryans
- Battle of 10 kings, near Purushni (Ravi river) : ‘Bharata’ tribe fought against 10 tribes and won
- Bharata = Bharatvarsha
- Bharat + Puru =Kuru
- Better weapons made of bronze, copper
- Used coat of mail (armour)
- They possessed chariot driven by horses
- No standing army
Economy of Aryans
- Pastoral life – cattle breeding primary occupation
- Agriculture secondary – wars were not fought over land but over cattle (Gavishthi)
- Crafts- pottery, leather goods, smiths
- No coins . Bartering or gift based economy
- Bali’ – voluntary gift to priests (cow/women)
- No taxes
- Only Copper, bronze mentioned
Religion and Philosophy of Aryans
The early Vedic religion was naturalistic. Evidently, there were neither temples nor idols. The mode of prayer was recitation of mantras. Sacrifice was offered for Praja (children). Pasu (cattle) and Dhana (wealth) and not for spiritual upliftment or misery
Natural phenomenon manifested in anthropomorphic forms
- Terrestrial gods – Prithvi, Soma, Agni
- Atmospheric gods – Indra, Vayu, Maruta
- Heavenly gods- Varun , Surya, Usha
Most Important gods – VARUN –god of sky, water
INDRA – god of war & thunderstorm , ‘purandar’
AGNI – god of fire
Prayers, sacrifices of milk, ghee, vegetables, grains along with hymns in proper order •
Gods were invited to partake in the sacrifices made •
Yajna (sacrifice) was performed along with chanting of Vedic hymns. •
People poured ghee and other ingredients into the fire to invoke the blessings of gods. •
Reason for Yajna- Asking for children(praja), cows(Gau) and food








No comment